Bluff Goes Big
The most attention-grabbing fact of the incorporation is its size: 38 square miles, which is more than 60 times the size of Bluff’s present developed footprint. The scale of the new boundary is fairly hard to contextualize, but one way to try is by linking it to population and housing estimates.
Bluff currently has a population of 265, a developed footprint of around 400 acres, and a residential stock of 184 homes including both household and non-household units (second homes, vacation rentals, etc.). Effective household size is therefore about 1 ½ people per dwelling unit and net residential density about one dwelling unit per 2 ¼ acres. Using these facts as analytical pivots, we can game out a few hypothetical scenarios about Bluff’s buildout.
For example, if Bluff were to continue to pursue a sprawling development pattern of, say, one home per two acres, a housing stock of about 12,000 units would fit within the new town limits. Assuming basically the same household composition as Bluff has today, this would spread a population of around 18,000 people across an area only a bit smaller than San Francisco (population 865,000).
If, on the other hand, Bluff were to grow according to a more efficient development pattern yielding a residential density of something like 5 homes per acre, the town could grow its housing stock 11 times over to 2,000 residences without expanding beyond its current developed footprint at all and could build over 120,000 residential units, almost 700 times more than it has today, before running out of land within town limits.
Of course the possibility of either of these thought experiments becoming reality is roughly zero. The Bluff Incorporation Feasibility Study projects an average population growth rate of about 0.5%, which equates to well under one new Bluff household per year. Even after accounting for residential demand for second homes and other non-household dwelling units, the study projects a need for less than two new homes per year.
Based on these facts, it is quite an understatement for the Feasibility Study to note that “[t]he proposed Bluff Town area has an ample amount of vacant land within the proposed boundaries.” After all, assuming even the sprawling development pattern that typically prevails in the New West, it would take thousands of years for Bluff to reach buildout at the study’s projected growth rate.
Given these conditions — minimal development pressure and abundant under-utilized land within Bluff’s existing footprint — the expansive Bluff boundary was obviously not established based on any sort of ordinary relationship between municipal incorporation and the provision of services to a discrete population, either now or in any conceivable future.
Non-Private Land
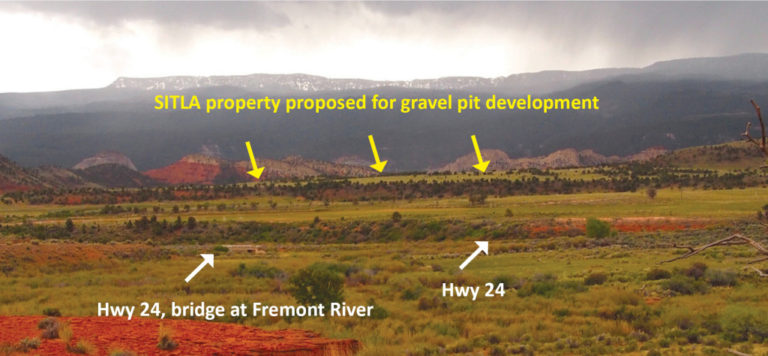
There is another unusual element about Bluff’s incorporation: the large amount of SITLA and BLM land encompassed within the new boundary. According to the feasibility study, of the 38 square miles contained within Bluff town limits, “SITLA and BLM lands will comprise 16.5 sq miles.” The straightforward reading of this statement is that about 43% of Bluff is non-private land managed by federal or state entities, leaving roughly 57% in private ownership. But even a cursory review of the incorporation map reveals that this cannot be the case, since the property color-coded as private is obviously much less than a majority of the land contained within Bluff boundaries.
To independently estimate the composition of land ownership, we can tally the number of township sections in each category. BLM land within the town boundary totals 12 sections in their entirety or near-entirety plus smaller portions of 11 additional sections. SITLA land also totals 12 sections in their entirety or near-entirety plus smaller portions of 7 additional sections. Since each section is one square mile, BLM and SITLA land therefore adds up to almost 24 square miles just counting sections that are entirely or almost-entirely within their ownership category, which is about 50% more than the 16.5 square miles referenced in the incorporation feasibility study. Once the partial sections are also accounted for, SITLA and the BLM may each manage something like the 16.5 square miles referenced in the study. If so, that would mean 33 of the 38 square miles inside Bluff boundaries are BLM or SITLA lands and less than 15% is private property.
Whatever the exact figures, the information in the feasibility study is a curious calculation and presentation of the composition of land ownership within Bluff’s new city limits, and begs further questions about the thought process that led to the new Bluff town limits. But before entertaining such questions, it may be instructive to make a short narrative and analytical detour.
The Wayne County Template
It is entirely likely that the Bluff residents who drove the boundary-drawing process are familiar with the experience of their New West antecedents, including in other parts of southern Utah. In particular, they may have learned some interesting lessons in land use realpolitik from a recent dispute in adjacent Wayne County. The facts of that controversy are as follows.
A local road construction company reached agreement with SITLA to undertake sand and gravel mining operations on a 120-acre trust land parcel located in unincorporated Wayne County near Teasdale. Consistent with its ordinary practice, SITLA required that the prospective mine operator secure local zoning approval prior to beginning operations. In this instance, that meant applying for both a zone change and conditional use permit (CUP). The construction company applied for the necessary approvals and the application was met with organized opposition from some area residents. Wayne County eventually concluded that it had no zoning authority over trust lands, and, on that basis, declined to take any action on the zone change application. The county went on to treat the CUP as an independent application and approved the conditional use permit.
The opponents of the gravel operation then sued and the trial court affirmed the county’s conclusion that local land use authorities lack jurisdiction over trust lands. Secondarily, the court disagreed with the county as to its handling of the CUP. (Because conditional uses are specific uses permitted within a specific zone, albeit with mitigation of negative impacts, issuance of a CUP cannot be severed from the applicable zone that permits the use in question. To properly approve the CUP, Wayne County would have had to also approve the rezone request.) In effect, the court held that when SITLA submits to local land use authorities, it is engaging in arguably useful but ultimately non-binding regulatory theater.
What happened next is interesting. Rather than allow the gravel operation to proceed, as the court had made clear was its right, SITLA canceled the mining lease. In doing so, SITLA cited one of the main arguments of the opponents of the application, namely, that the parcel may have become more valuable as a prospective residential subdivision than as a gravel pit.
SITLA then included the parcel in its semi-annual auction of properties deemed suitable for disposal and, in yet another twist, the property failed to attract a bid greater than the reserve price of $6,600/acre. Not from a prospective developer; not from the gravel mining company; and not from the opponents of the gravel mine who were adamant that the property be preserved in an undeveloped state. So far, SITLA has declined to say if or when the land may be back on the auction block and has also given no indication that the failure to sell the parcel has caused it to reconsider the canceled mining lease.
This episode underscores at least two conditions of land use in Utah: (1) the modern SITLA is not an ideological or partisan agency, but a professional technocracy that must carefully manage its public reputation while pursuing its legal mandate to generate revenue for the beneficial owners of trust lands; and (2) like well-heeled NIMBYs everywhere, amenity migrants wield considerable political power to tilt land use in the direction of their particular preferences even where they lack any legal authority to do so and despite operating within an ostensibly pro-productivist political environment.
And so, despite a few interesting wrinkles, this tale from Wayne County is pretty typical of rural gentrification across the Colorado Plateau. Land uses like grazing and resource extraction are especially disfavored by New West settlers, but really almost any land use has the potential to be opposed as a threat to the establishment of a bourgeois utopia. Of course the systematic replacement of industrial-age land uses and social values with their post-industrial counterparts enhances the saleability of the place to the next wave of middle-class amenity migrants who then add their influence to the rebranding campaign. Lather, rinse, repeat.
In this account of the process of rural restructuring in the West, generational blue-collar residents lose their grip on their home’s sociopolitical landscape by losing their grip on the physical landscape. But note that this shift is often as much a transformation of the symbolic, social meaning of the landscape as any significant change in its actual use. For example, rebranding the San Juan backcountry as “Bears Ears” changes almost nothing about the landscape in productivist terms, but completely changes its social and economic meaning along post-industrial middle-class lines. Note also that this revolution in sociopolitical status typically occurs well before incumbent locals lose their majority status at the ballot box. In the gentrifying New West, it is rule-by-the-few zoning, not elections, that defines most of the important terms of social and economic life. With this in mind, let’s return to Bluff.
SITLA’s Bluff Block
Most of the trust land within Bluff boundaries consists of a large contiguous block on the so-called Bluff Bench above town. This should strike the informed observer as unusual on its face. The typical distribution of trust lands is the same as existed at statehood, with sections 2, 16, 32, and 36 of each township belonging to particular named beneficiaries (mostly K-12 schools). This allocation explains the distinctive blue checkerboard on a typical map of Utah. When, instead of that pattern, you see a large block of trust lands like the one north of Bluff — aggregated to include multiple adjacent sections and located near roads and/or towns — it is the result of an intentional exchange transaction between Utah and the federal government. These generally take one of two forms:
(1) “In-Lieu” Lands. As mentioned above, the Utah Enabling Act granted to the state four sections of each township to be used for the financial support of education. However, Congress had already disposed of some of the specific enumerated sections and so the Enabling Act also stipulated that Utah would be entitled to take equivalent property of the state’s choice from other sections of available federal land. Utah completed its process of electing these so-called in-lieu lands over the course of about 20 years, beginning in the 1960s. (Unsurprisingly, this was not a smooth or linear process, but the details of related controversies are beyond the scope of this analysis.)
The Bluff Block is a particularly good example of how this wrinkle was ironed out. Sections 32 and 36 of the township in which Bluff is located (Township 40 South Range 22 East) are south of the San Juan River, which makes them part of the Navajo Reservation and therefore ineligible for inclusion in the state’s grant of trust land. In turn, this and similar withdrawals by Congress of lands across Utah triggered an election of equivalent federal land elsewhere as replacement state trust land. The Bluff Block appears to have been assembled in 1977 as one such election in this process of reconciliation. Given the productivity of the nearby Aneth oil fields during this period, it is almost certain that these sections were chosen for their fossil fuel potential. But as yet, after more than 40 years, there has been really no energy development on this particular tract of land and overall oil and gas production in San Juan County has steadily declined over that same period.
(2) Negotiated Exchange Lands. The completion of a negotiated exchange is typically triggered by a specific land use conflict. When this sort of exchange is successful at all, it usually involves a years-long process of painstaking negotiation and due diligence.
For example, when a large national monument like Grand Staircase-Escalante (GSE) or Bears Ears is created, the Secretary of Interior is directed to acquire the trust land locked within the new monument’s boundaries through an exchange of other federal land of equal value. In the case of GSE, the monument boundary encompassed around 176,000 surface acres of trust lands (and 24,000 acres of subsurface mineral rights), which eventually led to a legislated land swap: SITLA exchanged a total of about 377,000 acres (its GSE inholdings along with other trust land located within National Parks, National Forests, and Indian reservations) for $50 million and about 139,000 acres of federal land. Noteworthy blocks of land acquired by the state through this exchange included a massive tract surrounding Big Water near Lake Powell (a corner of which is now home to Amangiri) and land with high mineral potential in the Uintah Basin.
Such exchanges are often hailed as win-win propositions by productivists and post-productivists alike, and in some respects they certainly count as that. After all, a negotiated exchange represents a far more constructive treatment of Utah’s vast non-private lands than the state of “total warfare” that typically prevails. And if we as a society accept the premise that some places are more worthy of conservation than others, it probably follows that resource extraction and other industrial uses should be concentrated in some areas rather than others (not to mention the fact that economic value, whether related to agricultural, industrial or recreational uses, is not equally distributed across non-private lands). But the careful observer may note that there are contradictions lurking here.
Cornering SITLA
It may also, by this point, occur to the careful observer that SITLA and rural Utah counties are increasingly placed in a difficult predicament by two major political and economic forces. The first is the shift by the U.S. government from a policy of acquisition and disposition of federal land to one of retention. Starting no sooner than the passage of the Taylor Grazing Act in 1934 and ending no later than passage of the Federal Land Policy and Management Act in 1976, the federal government first tacitly then explicitly ended its policy of non-retention of federal public land. In numerical terms, 816 million acres of public domain land was conveyed into private ownership between 1781 and 2006, 97% of which occurred prior to 1940.
One of the results of the timing of this policy shift relative to Utah’s existence as a state is that federal land policy de facto applies not just to federal land, but also to most Utah state trust lands, which amount to roughly 3.4 million acres or 6% of Utah’s land mass. SITLA has a constitutional mandate to use the land under its management to generate revenue for Utah’s schools, but its ability to do this is significantly constrained by the scattered nature of SITLA’s holdings combined with direct federal ownership of 2/3 of Utah. This combination means that most trust land is persistently locked within larger tracts of federal lands, which are managed according to entirely different legal paradigms and for entirely different purposes. The practical effect is that the federal government indirectly controls more non-private land in Utah than it owns outright in 35 other U.S. states.
The second major political and economic force painting SITLA and many rural Utah counties into a difficult corner is the colonization of the rural West by the post-industrial professional-managerial class. This is the Wayne County example, in which, despite a lack of local jurisdiction, zoning decisions heavily influenced by amenity in-migrants bend the use of trust land toward the creation of a sprawling, gentrified New West. If extractive or industrial land uses are taken completely off the table, and an area is instead marketed for its value as a New West enclave, the only viable alternative that remains to SITLA is to sell or otherwise develop their holdings for residential, resort or similar purposes.
Moving the Goal Posts
Recapping in chronological order each key trend or event in the life of SITLA’s Bluff Block provides an interesting example of the interplay of these dual forces in real, historical terms.
For our purposes, the beginning of the story was Utah statehood and the grant of four sections of each township to be managed according to trust principles for the benefit of Utah’s schools. Over the ensuing 80 years, federal land policy shifted from disposition to retention. Then, in 1977, Utah selected the Bluff Block as an in-lieu exchange tract. Beginning in earnest in the 1990s, New West gentrification spread across canyon country and, not coincidentally, escalating arguments over public lands became a constant feature of the region. And so, by the 2010s, with a Democratic President in the White House, Bluff had become a natural beachhead for the final push for a massive national monument designation in San Juan County.
As various competing maps were drawn during the lead-up to Obama’s proclamation, some monument advocates included SITLA’s Bluff Block within their proposed boundaries. At first blush, this made little sense: the Bluff Bench has limited archaeological or scenic value and looping all of it into monument boundaries required a lone, notable incursion east of Highway 191. But some Bluff residents apparently reckoned they could persuade the Obama administration to stretch the purpose of the Antiquities Act to include its use as a potent method of local zoning. And so, at the end of 2016, most of the Bluff Block was indeed encompassed within the monument boundaries as a result of this lobbying.
(For their part, Diné Bikeyah did not include the Bluff Bench in their 2013 proposal. In fact, their boundary along the east of Comb Ridge essentially matches the eventual “Hatch Memo” boundaries.)
This inclusion of SITLA’s Bluff Block within the 2016 monument glossed over the fact that this tract of land is not only not federal land, but is trust land previously acquired by Utah in exchange for other federal land elsewhere in the state. Pro-monument folks extol the virtues of state-federal exchanges when it’s convenient, but will endlessly demagogue SITLA the rest of the time and even attempt to recapture or otherwise block the use of the very trust land previously acquired by Utah in state-federal exchanges.
Drawing Conclusions
All of this history and nuance remained unacknowledged by The New York Times (and the many other news outlets who picked up their coverage) when they recently published documents describing how, as one of the final chapters in the story so far, SITLA’s Bluff Block came to be removed from monument boundaries as part of the Trump-Zinke boundary reduction.
There has also been, as far as I can tell, no recognition that incorporating something like 33 square miles of non-private property into Bluff town boundaries is a variation on the tactic of including that land within monument boundaries. In terms of blocking disfavored land uses, what may or may not ultimately be accomplished in this instance through use of the Antiquities Act is likely to be fairly easily achieved through garden variety NIMBYism as expressed in the local zoning context.
After all, given the endless national controversy surrounding Bears Ears and local zoning dynamics typified by the Teasdale gravel-mine-that-wasn’t, there is now no realistic scenario in which SITLA will ever lease its Bluff Block for energy development or any other significant industrial purpose. Nor is any other economically productive use of the land likely except maybe, someday, hospitality or residential development. That scenario also seems highly implausible given the character of the land in question, but if it does occur, it will be entirely because of demand created by the marketing of Bluff as a New West enclave.
This is how a small group of self-serving residents, with significant help from their non-resident allies, will successfully dictate the use of thousands of acres land they do not own and which is not subject to their zoning authority. Such control will either be a superfluous constraint on non-productive lands or will cost San Juan County and the State of Utah millions of dollars in school funding and property taxes.
_____
Select sources & additional reading:
- Andrus v. Utah, 446 U.S. 500 (1980).
- Lassen v. Arizona Highway Dept., 385 U.S. 458 (1967).
- Harmer, M. Utah’s School Trust Lands: A Century of Unrealized Expectations. BYU Journal of Public Law.
- Utah School and Institutional Trust Land Administration. Land Exchange Distribution Account (LEDA). Presentation at June 2016 SITLA Board Meeting.
- Kirkegaard, M. Land Exchanges and Public Lands Bills in Utah. The Hinckley Journal of Politics.
- Utah Schools and Lands Exchange Act of 1998. Section 2.(2) “The parties agreed at the outset of negotiations to avoid identifying Federal assets for conveyance to the State where any of the following was known to exist or likely to be an issue as a result of foreseeable future uses of the land: significant wildlife resources, endangered species habitat, significant archaeological resources, areas of critical environmental concern, coal resources requiring surface mining to extract the mineral deposits, wilderness study areas, significant recreational areas, or any other lands known to raise significant environmental concerns of any kind.”









I wonder where the water for the inevitable golf courses and housing subdivisions will come from. The San Juan has always been capricious in its flow. Lake Navajo is a water users lake, providing irrigation for the farmers in Bloomfield and Farmington. Leaving little for a “New Moab” unless water rights have been established. And just where does this new tourist mecca of Bluff propose to dispose of all the tourists p**p. Moab can’t dispose of the waste from Arches and Canyonlands, It has to be trucked to Wellington or Price for proper disposal. I’m pretty sure Kayenta, Mexican hat, Teec Nos Pos are not going to accept the sh*t. Which leaves possibly Farmington, and somehow I don’t think they’re going to accept it without a hefty fee. And then it all goes back into the San Juan.
A new Moab (Moab Jr?) was inevitable. The pressure for it is like a Borg invasion–you must comply. Even Green River now has a cafe with bicycles and kayaks attached to the facade. To think that corporate interests aren’t interested in the amenities economy would be naive. I don’t like it, but I’m not surprised. Hopefully the practical limitations of development (water?) will slow this down. But it never slowed down development in Colorado. Why should Utah be any different? Will Mormon farmers hold on to their agriculture water in the face of corporate money making them wealthy?
@Bill Crowder:
I’m sorry you missed the point of the piece. That’s probably my fault. Let me see I can give you a better road map.
New West gentrification does not simply happen. If it is inevitable, it is not inevitable in the same way gravity is inevitable, but more like the way the displacement of indigenous people was an inevitable step in creating both urbanized America and the American wilderness. Or, to make a more contemporary comparison, New West gentrification is quite similar to urban gentrification, but whereas urban gentrification is a heavily scrutinized phenomenon, the rural variant has received very light coverage. In fact, as far as I can tell, the Zephyr is the lone publication willing to consistently cover this beat as the New West’s colonization of canyon country has gathered steam over the past 30 or so years.
So, my intent here was not to “parse out some nefarious plot,” but to lay bare certain pulleys and levers of power that are integral to the rural restructuring of canyon country (and beyond), and to examine how these pulleys and levers are being operated in the case of Bluff. I’m not suggesting that the folks living in Blanding and Monticello are heroes, and the folks in Bluff villains. These things are slightly more complex than that.
That said, local planning and zoning — Bluff’s incorporation being the specific example under the microscope here — is really where the trench warfare to transform canyon country is fought, and such issues are almost never considered within a larger social, political or economic context. You think this piece is overthinking the dynamic; I think it barely scratches the surface.
Obviously, a couple of the specific entities New West gentrifiers typically wrestle with in southern Utah (at least initially) are a county government that’s at least somewhat antipathetic toward their goals, and also, like it or not, SITLA. So that’s where an analysis like this tends to go. The reasons I didn’t talk to Bluff people are because I’m a land use attorney not a journalist and because, frankly, none of what’s relevant here depends very much on what you think you’re doing. It depends on what you are actually doing.
If we lived in a perfect world Bluff would not have needed to extend land boundaries, however we live in San Juan County where it is not perfect. To help prevent another Moab or in the future Spanish Valley, the citizens decided that a large foot print was required. We want to help determine our growth patterns in the future rather than the indifferent county authorities. The state is looking at placing a gravel pit in my backyard, although we can see 3 from my porch. Like Torrey, should not the citizens who live in an area have a say in development rather than county folks who want money from taxes? It seems important to recall that local control is better than federal, state, or county. Is that not what the Sagebrush Rebellion was all about? All you have to do is look at a recent development in Bluff, where the county approved the plan and then came to the taxing authorities to give up taxes to help the developer complete his project. A redevelopment agency in a town of 300? So give Bluff a chance to disprove your concept that we are not able to provide growth in a reasonable manner. POWER TO THE PEOPLE
Dear Wes–you’ve thrown down the gauntlet! You say (essentially) that Bluff locals will never allow it to become another Moab or Spanish Valley, that local control is better than federal. I’m not so sure, since federal control represents the interests that all Americans might have in the preservation of the canyon country and local control usually represents a means to generating a dollar. But sure, I guess outsiders like me are willing to give you (and Bluff) a chance. I mean, what choice do we have anyway? If Bluff can both thrive and prevent Moabization in the process, then you can say “We told you so”.
@Wes Shook:
Thanks for taking the time to comment. It sounds like we agree that the point of the large Bluff boundary is to wrest control over as much land as possible from the county and state. I’m sure we also agree that Bluff residents have the best of intentions for the future of the town. Where we may start to disagree is if we tried to define what “success” for this project even means.
Here’s a little thought experiment. Someone said in a Zephyr comment thread the other day that they’d prefer all the cars lined up at the entrances to Arches and Zion like they always are these days to a single pump jack. Can you at least see how a reasonable person might have the opposite preference?
I think it’s also worth lingering over the general question of why certain attitudes, behaviors and land uses are so completely repugnant to New West settlers while certain others are accepted or encouraged.
Anyway, the available evidence strongly suggests that Bluff lying within San Juan County doesn’t matter as much as you might think. I’m not sure Castle Valley really has bragging rights over Spanish Valley, and yet Grand County was controlled by New West elites by the early 90s (see the link at bottom for an illuminating bit of time travel on the topic).
More broadly, few places are zoned as tightly as, say, Springdale, Jackson, Telluride, Park City. And they are all, to one degree or another, basket cases. Like Evan says, if Bluff manages to be the first town to put its hand in the fire without getting burned, you definitely should remind us that we doubted it could be done.
http://www.canyoncountryzephyr.com/2014/02/03/from-the-zephyr-archives-an-interview-with-grand-county-councilman-bill-hedden-by-ken-davey/
Re: what will become of Bluff. If the town and its city council ask themselves the question, “what would Gene and Mary do”, before they act then there might be some hope in Bluff not becoming Moab.
The cost of housing and land is already going through the roof for a town in the middle of nowhere and development is already beginning to happen. I am cautiously optimistic and hope I am not being delusional given the history of the rest of the “the new west”.
PS to the above: If the good citizens of Bluff read Tonya Stiles “Sowing Clover” column in this issue of the Z it couldn’t hurt either.
@Stacy Young,
Thanks for the perspective. A couple things stand out for me. I pretty quickly went to the map to confirm what I think is a pivotal lever for at least some Bluff locals: the pioneer track over Comb Ridge. One of the more idiosyncratic land use debates surrounds the commercialization of the route of the Hole in the Rock settlers, and it appears from the southwestern extension of the boundary proposal that Bluff intends to get their ‘fair share’ of the story. Any thoughts?
The simple scarcity of developable private land in Utah would increase the value of SITLA tracts, once trades can be negotiated. It is a complicated process to trade property with the Fed, but Utah schools stand to cash in if it’s done right.
And this is just gold – “they’d prefer all the cars lined up at the entrances to Arches and Zion… to a single pump jack.” Maybe that’s all that’s needed to inoculate the West against yuppification. Serious NIMBY irony, there.
To Joseph’s naive hope for Bluff: “what would Gene & Mary do” suggesting they always did the right thing. As a longtime resident who had to redo Foushee’s no-code plumbing, wiring, septic, waterlines, basic construction, etc, their name became a ‘verb/adverb’ in building/construction (e.g., as in “damn, don’t Foushee that!”). Foushee’s were not saviors, they just tried to make do and capitalized quite nicely in buying land and falling down properties for next to nuthin’ and rebuilding in highly questionable ways, like light switches inside shower stalls, toilet paper hangers over bathroom heaters, etc.
Comments regarding why the big parcel of State lands on Bluff Bench? and why the Navajo boundary lies north of San Juan River @ Montezuma Creek-Aneth (tied to Stiles Take It or Leave It, Media Bias article in this issue). Must go back to BIA (1905) creation of “Paiute Strip” reservation for Paiutes south of San Juan River and east to about the 110th Meridian. It included Navajo Mtn and the as yet “undiscovered” Rainbow Bridge.
The Paiute had no Fed agency of their own. In early 1920s when Albert Fall was Sec. of Interior (and of Teapot Dome fame) the BIA reported falsely that the San Juan Paiute were not using their reservation & in July, 1922 the strip was returned to public domain. The Navajo wanted the Paiute Strip added to the Navajo Rez. In 1933 the Paiute Strip was made part of the Nav Rez, and part of this realignment led to the Rez boundary extending to the north of SJ River at Aneth where in 1956 Texaco hit big oil that led to development of Aneth oil field – almost entirely within new boundary of Nav Rez. BLM and Nav’s got royalties, but State of Utah got little. Stiles mentions some payment to Nav Rez in this issues “Take it or Leave it – Part I,” but they also were paid several times since the 1950s for readjustments in royalties. In total, the Navajo Nation has been paid many, many hundreds of millions of $$ – But most of the money went to Window Rock and/or lined numerous Navajo leaders pockets [Washington DC bureaucrats taught them well]. BUT, the State of Utah missed out almost entirely on a Billion barrel oil field in agreeing to this realignment.
Then, along comes Lake Powell (1963) and followed by Glen Canyon Recreation area (1972) and by golly, this time the State wasn’t going to miss out. But the BLM geologists and most State Geological Survey geologists are NOT savvy about subsurface geology. Few ever worked in the petroleum industry and didn’t understand the fundamentals of what to look for wrt what makes an oil field. Most governmental geoscientists of that era had nary a clue, and many still don’t. The Utah GS is far better today than in the 70s or 80s. But, between the Feds and State, they thought that by stock-piling a big contiguous swath of State lands that were going to be flooded by Lake Powell they would benefit from “the next Aneth!” But – It didn’t. It won’t. It will never be – at least from an oil and gas standpoint. Simply put, the rocks aren’t right, there’s not the necessary presence of source/seal or trap [the basic Big 3 in oil exploration]. And same for uranium! Not here!
The value of Bluff Bench has been grazing land (as is the case today); future might be “Bluff Bench Estates” – but water becomes issue from bedrock aquifer and Bluff has twiddled around so long on proving up their right to San Juan River water, that this resource may have gone downstream or diverted upstream. The bench doesn’t have the big gravel resources that the valley has. Scare tactics were used to incorporate the blob of State lands to prevent…..what? Cows or Condos? Probably no pump jacks or cars all lined up. Just a REALLY BIG city limits to manage.
[…] ahead of the horse and county institutions are in “react mode.” Concrete consequences include Bluff’s absurd new city limits and now the school board struggling to find a sound basis from which to set tax-subsidy […]